The way the vision system works is detailed. For a simple explanation, we see with our brain, not our eyes. Think about looking at a tree. Light bouncing from the tree travels through different parts of each eye to focus on the retina at the back of each eye. Cells in the retina turn the light bouncing from the tree into electrical signals. Those signals travel along the optic nerve to the brain. Each eye receives separate information about the tree. The brain combines the two images from each eye into one image and we “see” the tree.
To have good vision, at least four things must occur. The
- Eyes must be healthy.
- Visual pathway from the eyes to the brain must work correctly.
- Eyes must be straight, and
- Images sent to the brain from each eye must be in focus.
Certain problems can interrupt the four things needed for good vision, especially during when a child’s vision system is developing.
Some of these problems happen only during early childhood, such as amblyopia, which can lead to permanent vision loss if not found and treated early.
The main reason for vision screening of young children is to look for amblyopia, or vision problems that can cause amblyopia. Let’s look at definitions, videos, webcasts, and handouts about early childhood vision disorders.
This picture shows parts of the eye talked about in the definitions:
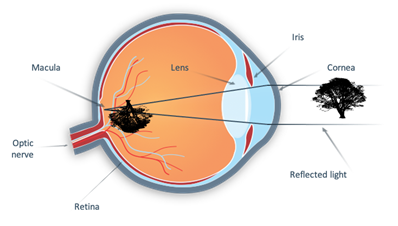
For more information on the eyes and how we see, visit “The Eye & How We See” at Prevent Blindness. https://preventblindness.org/eye-how-we-see/ A video from the National Eye Institute, called “The Visual System: How Your Eyes Work” is available at: https://youtu.be/i3_n3Ibfn1c
Refractive Error
Light rays bouncing from an object, such as a tree, are bent, or refracted, to land on a specific location on the retina at the back of the eye.
A “refractive error” occurs when the parallel light rays are not focused directly on a specific location of the retina.
Nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), astigmatism, and anisometropia are “refractive errors”.
Anisometropia
an-I-suh_MA-tro-pee-ah
Anisometropia is a refractive error. It is a difference of refraction between the 2 eyes.
One eye may be more farsighted or nearsighted than the other eye.
Or, one eye may be farsighted, and one eye may be nearsighted.
Hyperopia
hi-pur-OH-pee-uh
Hyperopia is a refractive error. Hyperopia is the medical term for farsightedness.
The eyeball is usually shorter than normal, which makes it difficult for light rays bouncing from an object to land directly on a specific area of the retina at the back of the eye.
A child with hyperopia will have difficulty focusing clearly on close objects.
Notice the picture of the child on the swing is blurred, but the child pushing the swing is clear.
Think “clear at far, fuzzy at near”.
Myopia
mi-OH-pee-uh
Myopia is a refractive error. Myopia is the medical term for nearsightedness.
The eyeball is usually longer than normal, making it difficult for light rays bouncing from an object to land directly on a specific area of the retina at the back of the eye.
A child with myopia will have difficulty focusing clearly on distant objects.
Notice the picture of the child on the swing is clear, but the child pushing the swing is blurred.
Think “clear at near, fuzzy at far”.
Astigmatism
uh-STIG-muh-tiz-um
Astigmatism is a refractive error,
The cornea at the front of the eye is rounded, similar to the curve of a basketball. The cornea of an eye with astigmatism is shaped more like a football.
Light rays do not focus directly on a specific area of the retina at the back of the eye. Instead, the light rays land on different parts of the retina. This causes blurred vision at any distance.
Notice both children are blurred.
Strabismus
struh-BIZ-mus
A condition in which the eyes are not straight. The eyes are misaligned.
Sometimes strabismus is called “lazy eye”, but this is wrong. “Lazy eye” is another name for amblyopia.
For a child with strabismus, one eye will appear straight while the other eye turns inward, outward, upward, or downward.
When strabismus occurs, the brain receives two different images from eyes that are so different the brain cannot combine the two separate images from each eye into one image.
More information about eye terms and vision conditions are available at:
- Prevent Blindness – https://preventblindness.org/glossary/
- American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus – https://aapos.org/patients/eye-terms
- American Optometric Association – https://www.aoa.org/patients-and-public/eye-and-vision-problems/glossary-of-eye-and-vision-conditions
- American Academy of Ophthalmology – https://www.aao.org/eye-health
- National Eye Institute – https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/nei-for-kids/glossary
Videos, Webcasts, and Handouts:
- What is Amblyopia? – American Academy of Ophthalmology – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fI9P7NU98EE&feature=youtu.be
- Amblyopia, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment – Medical Centric – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eLbmk1Go8YQ&feature=youtu.be
- Amblyopia – American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_wMs-W515XA&feature=youtu.be
- Strabismus – American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=993C_P00_y4&feature=youtu.be
- What is Strabismus? – American Academy of Ophthalmology – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CAiawXTk3Zo&feature=youtu.be
- Answers to 8 Parent Questions About Myopia – Prevent Blindness – https://nationalcenter.preventblindness.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/22/2020/05/10-FS115-ENG-8answers-myopia.pdf
- The Visual System: How Your Eyes Work – National Eye Institute – https://youtu.be/i3_n3Ibfn1c
- Learn About Eye Health – NEI for Kids – National Eye Institute – https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/nei-for-kids




